Solder bead control methods in high-density pcb assembly
- Addtime: 2025-07-02 / View: 148
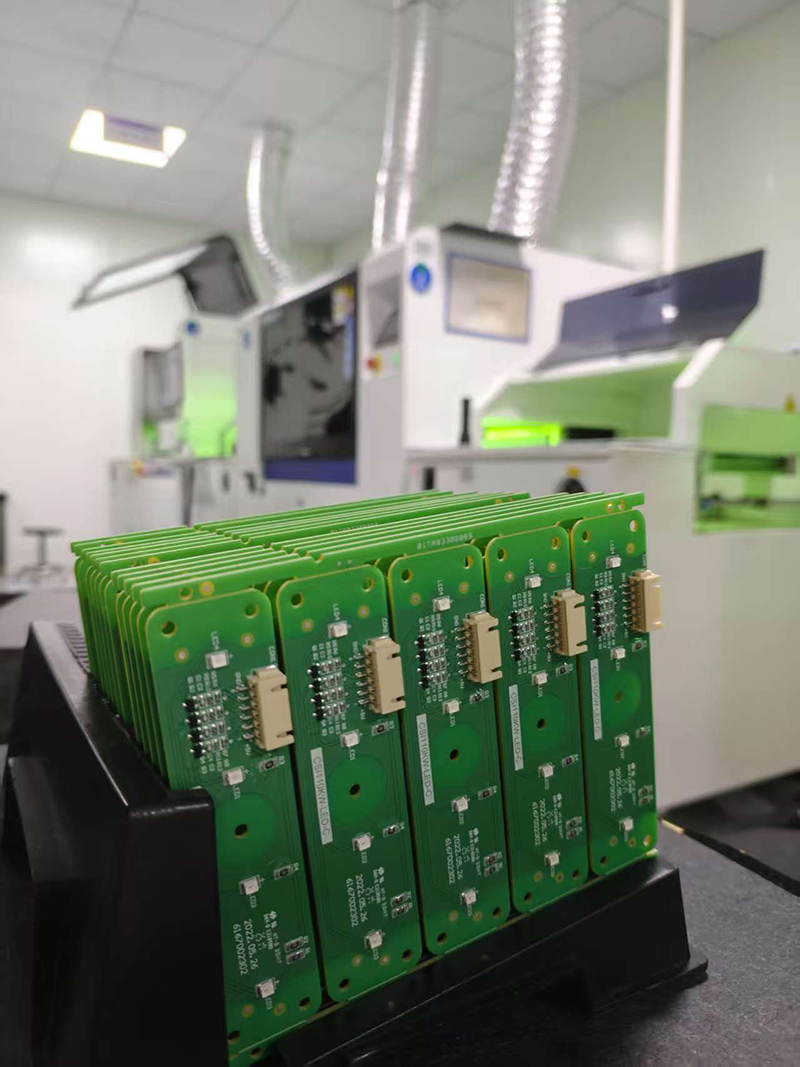
The control of solder balls in high-density PCB assembly requires a multi-faceted approach, mainly including solder paste printing, component placement, reflow soldering process, and PCB design. The following are detailed control methods:
- Solder Paste Printing Control
Select appropriate solder paste: Choose solder paste with good anti-collapse performance and select the appropriate solder powder particle size and flux formula based on PCB design and component type.
Optimize printing parameters: Adjust the squeegee pressure, speed, and angle to achieve a uniform and consistent solder paste printing thickness and shape, avoiding excessive or insufficient solder paste.
Stencil design: Optimize the stencil opening design to prevent oversized or irregular openings that may cause excessive or uneven solder paste.
Stencil cleaning: Regularly clean the stencil to prevent solder paste residue, which may affect subsequent printing quality.
- Component Placement Control
Placement pressure: Avoid excessive placement pressure that may squeeze solder paste outside the pads, leading to solder ball formation during reflow soldering.
Placement position: Ensure precise component alignment to prevent misalignment that may cause solder paste outside the pads to melt during reflow soldering, resulting in solder balls.
- Reflow Soldering Process Control:
Temperature profile: Optimize the reflow soldering temperature profile to ensure complete solder paste melting and control the heating rate and peak temperature to prevent solder ball formation.
Nitrogen protection: Use nitrogen protection during reflow soldering to reduce oxidation and improve soldering quality.
Cooling rate: Control the cooling rate to prevent uneven heating of solder joints and the formation of solder balls.
- PCB Design Control:
Pad design: Optimize pad design to prevent oversized or irregular pads that may cause excessive or uneven solder paste.
Solder mask design: Ensure that the solder mask aligns with the pad edges to prevent solder mask coverage of the pads, which may affect soldering quality.
Spacing design: Reasonably design component spacing to avoid excessive component density that may lead to poor soldering and solder ball formation.
- Other Controls:
Equipment maintenance: Regularly maintain and calibrate printing machines, placement machines, reflow soldering machines, etc., to ensure equipment accuracy and stability.
Personnel training: Provide professional training to operators to familiarize them with the operation process and control methods for solder balls.
Process inspection: Conduct visual inspections of PCBs after reflow soldering to promptly identify and address solder ball issues.